Are you experiencing slow internet speed or connection issues? If so, then you may be dealing with network latency. It is the time it takes for a packet of data to be sent from one point to another. In this blog post, we’ll discuss what network latency is, its common causes, and the best ways to reduce it.
So, if you’re looking for ways to improve your internet connection, keep reading!
What Is Network Latency?
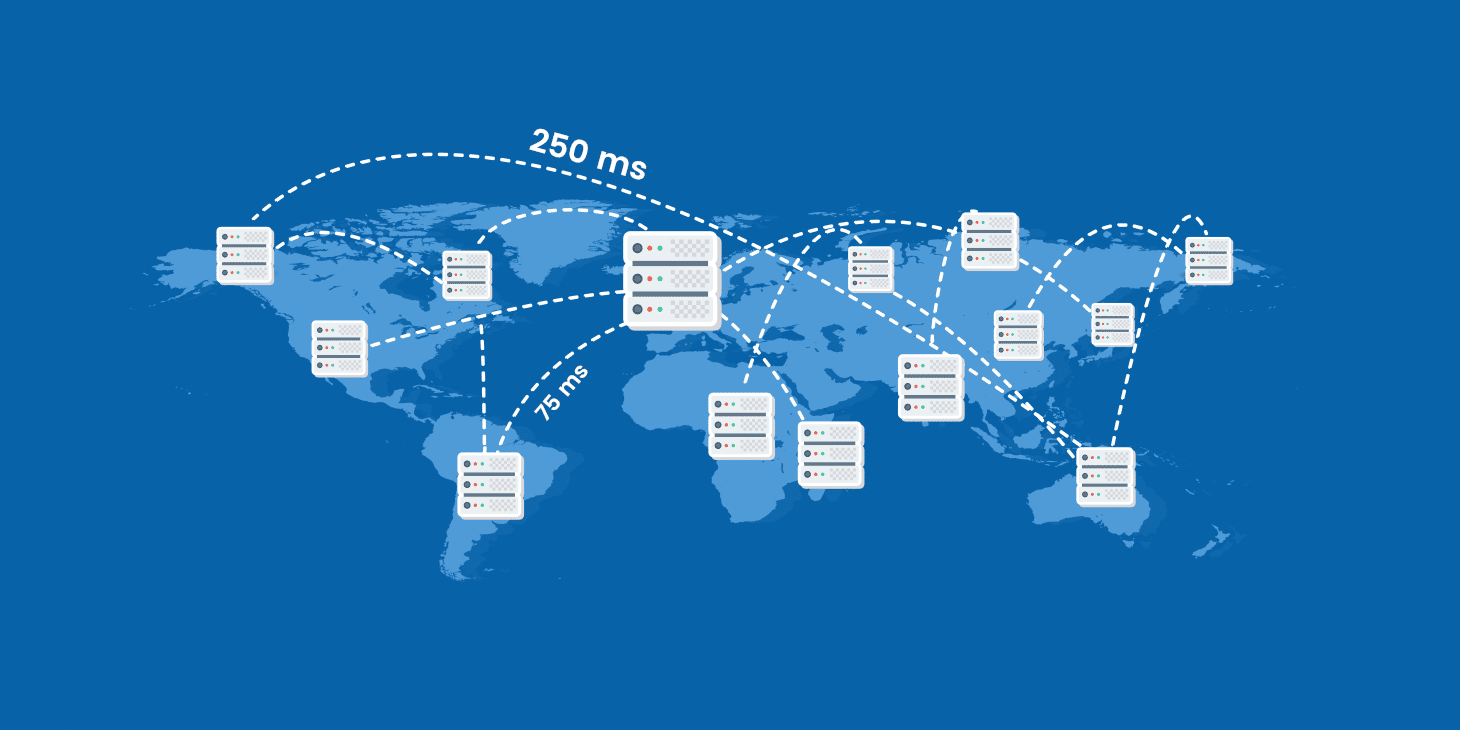
Network Latency is a measure of the amount of time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) and is the main factor affecting the performance of networks and applications that rely on them.
It can be affected by a variety of factors such as network congestion, hardware limitations, and geographic distance. is an important factor in determining the speed and performance of a network.
For example, if a website is located in a different country than the user, the latency will be higher than if the website was located in the same country as the user. Additionally, if there is a lot of network congestion, the latency will be higher than if there were no congestion. Understanding the concept of network latency and how it affects network performance is essential for optimizing network performance.
How Does It Work?
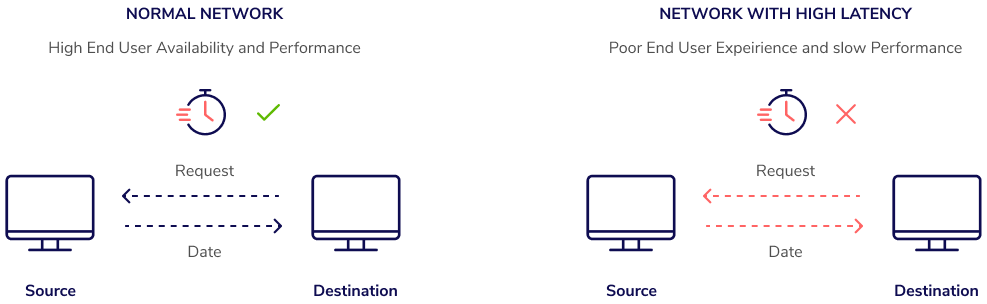
Network latency is an essential factor for real-time applications such as streaming video and audio, gaming, and VOIP. When it is high, it can cause delays in the delivery of data and poor user experience.
Network latency is affected by many factors such as physical distance, line speed, routing, protocol overhead, and congestion. Each layer adds a small amount of latency as data passes through different networks, routers, and switches. The more congested a network is, the more latency will be added.
Additionally, if there are any hardware issues or software issues with the network, the latency can increase dramatically. When using wireless networks, signal strength can also affect latency.
Therefore, understanding and reducing Network Latency is important for ensuring efficient network performance.
Why Does It Matter?
- It can have a significant impact on the performance of an application or system, as it can affect the speed and reliability of data transmission.
- It can cause disruptions in the communication between two systems or devices, leading to delays in loading webpages, streaming content, and other data-intensive activities.
- High network latency can also result in increased packet loss and higher packet error rates, further reducing performance.
- Poor network latency can also lead to an increased delay in voice and video calls, making communication more difficult.
- It can also increase costs, as it can cause delays in delivering services, resulting in fewer customers being serviced and lower customer satisfaction.
What Are the Common Causes?
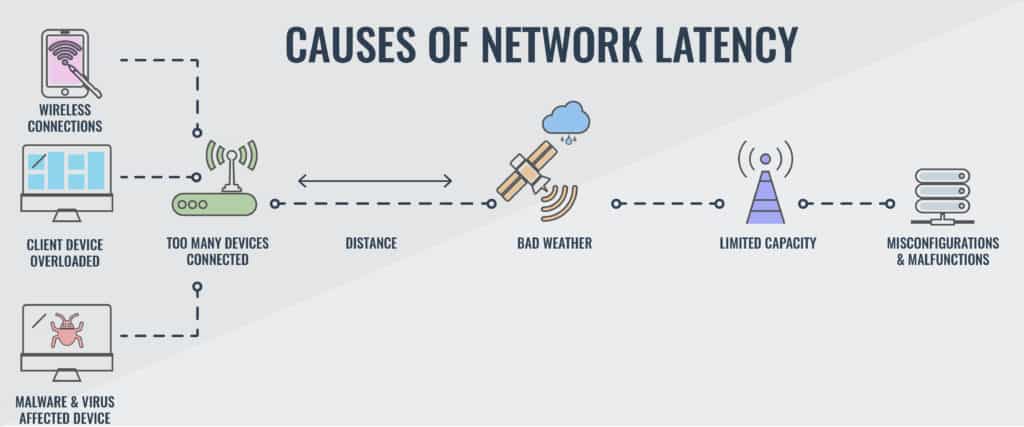
It can be a major cause of disruption and frustration when trying to access websites and applications. A few common causes are DNS server errors, poorly optimized backend database, low memory space, selection of transmission mediums, multiple routers, distance, and heavy traffic.
DNS Server Errors:
A DNS server (Domain Name System) is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. When a user types in a domain name, the request is sent to the DNS server which then looks up the corresponding IP address.
If the DNS server has an issue, it can cause network latency as the website may not be able to be accessed until the problem is solved.
Poorly Optimized Backend Database:
Many websites and applications use databases to store data. If the database is not optimized correctly, it can cause network latency as the server must query the database for information.
Low Memory Space:
Low memory space on a server can also cause network latency. If the server does not have enough available RAM, it cannot process requests quickly which can result in slow page loading times.
Selection of Transmission Mediums:
The choice of transmission mediums can also impact network latency. The type of cable used to connect the server to the network and the distance it needs to travel can affect the speed at which data is transferred.
Multiple Routers:
If a website or application uses multiple routers or switches, it can cause network latency as data must travel through each router before it reaches its destination.
Distance:
Network latency can also be affected by distance. If the server is located far away from the user, it will take longer for data to travel between them which can cause slower loading times.
Heavy Traffic:
Heavy traffic on a website or application can also cause network latency as there may be too many requests for the server to handle. This can cause delays in loading times or even complete outages.
Weather:
Bad weather can have a drastic effect on network latency, as heavy storms or strong winds can disrupt the signals sent between servers and devices. Any interference to the network connection can result in longer response times, making it difficult to access data or stream videos.
The degree of impact of the weather on network latency depends on the type of technology being used to connect devices; satellite connections tend to be more affected than cable or fiber optic networks.
Additionally, if the equipment is not properly shielded, extreme temperatures can affect the quality of the connection, resulting in a slower response time and increased Network Latency.

How Can You Reduce It?
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
One of the most effective ways to reduce network latency is to use a Content Delivery Network (CDN). A CDN works by distributing your website’s content across a network of servers located in various locations. This allows visitors to access your site from the closest server, significantly reducing page loading times.
HTTP/2
HTTP/2 can also help reduce latency. This protocol provides faster performance than its predecessor, HTTP/1.1, by allowing more requests to be sent at once. It also reduces the amount of data transferred and speeds up the transmission of data over encrypted connections.
HTTP Requests
Reducing the number of external HTTP requests is also important for reducing latency. Whenever a web page needs to make an external request, it needs to wait for the response before it can continue loading.
Prefetching Methods:
If there are too many external requests, the page may take longer to load and increase latency. You can reduce the number of external requests by using prefetching methods such as preconnected and prefetch.
This allows browsers to anticipate and prepare for external requests ahead of time, thus decreasing latency.
Browser Caching
Using browser caching is also important for reducing latency. Browser caching stores static files in a visitor’s browser so they don’t need to be downloaded from the server again. This speed up page loading time and reduce network latency.
How To Test It?
Testing network latency is important for understanding how quickly data is being sent and received. There are several ways to measure
One of the most common tools is ping, which tests the time it takes for a packet to be sent from one point to another. Another option is to use a traceroute utility, which will measure the time it takes each router along the way to respond. Additionally, you can use specialized software such as Path Analyzer Pro or Network Time Protocol (NTP) to measure it.
If you need more detailed information, you can use performance monitoring tools such as NetFlow Analyzer or Bandwidth Monitoring tools to determine the exact cause of any Network Latency.
If you don’t have access to any of the specialized tools mentioned above, you can also measure it by manually pinging websites or other internet-based services.
For example, you can measure latency between two computers on the same network by pinging a local IP address or website. You can also use an online tool such as the Network Latency Tester to measure latency from your computer or device to a server located in another part of the world. This can help you understand how your network is performing over long distances.
Conclusion
Network latency is an essential part of any internet connection and it can have a huge impact on the overall user experience. Understanding the causes, as well as the best ways to reduce them, can help you ensure that your network remains reliable and fast. Testing is an important step in ensuring that any potential issues are identified and rectified promptly. With proper maintenance and monitoring, you can keep your network latency low and maintain a satisfactory connection speed.