Introduction
Humans have needed improved ways to store and access data since the dawn of trade and commerce. The hard drives and servers are capable of storing, processing, and retrieving large amounts of data quickly, and easily. Public and private clouds
Hard drives and servers, on the other hand, have their limitations, and with the speed at which today’s enterprises and industries are developing, the need for storing data and management of large volumes of data has become a priority. This is where Cloud Computing can help!
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a network of more than one server that stores and retrieves data on the internet. Servers, databases, software, cloud storage, and networking are some of the IT operations available using cloud services.

Cloud Computing is a virtual platform that allows you to store and retrieve data through the internet without any restrictions.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Companies can rent access to everything from applications to storage from a cloud service provider instead of owning their computing infrastructure or data centers.
It is easier to understand the workings of a cloud computing system if breaking it into two parts: the front end and the back end.

The client’s computer or network is the front end. the application is additionally needed to access the cloud system. All cloud computing systems don’t need to have a constant user interface. The ‘cloud’ section of the system is the back end.
Any computer software, from data processing to video games, can be a part of a cloud computing system. every program will, in most cases, have its servers.
Types Of Cloud Computing Services
There are two main types of Cloud Computing services:
- Public Cloud
- Private cloud
What is Public Cloud?
The public cloud is a shared service that anyone with an internet connection can access. Multiple users can use the same storage within the public cloud at the same time. Businesses, colleges, governmental institutions, etc. operate the public cloud.
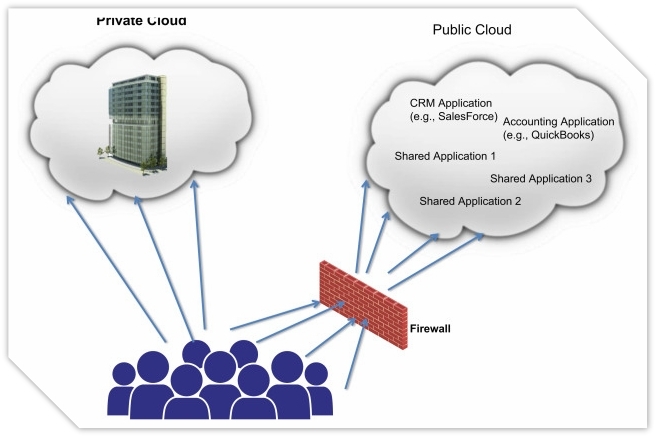
What is a Private Cloud?
Infrastructures are often hosted in private Cloud in third-party data centers. A single client is allotted to a personal cloud.
As a result, they provide a variety of security, management, flexibility, cost savings, and control advantages. These benefits are especially useful to organizations with consistent workloads or custom-built requirements, likewise to those in regulated industries.
Who Can Use Private Cloud?
They are excellent for a wide range of companies, from large enterprises in need of massive data storage to government agencies needing secure surroundings through which to carry out sensitive activities.
Private cloud corporations are more seemingly to be able to utilize their resources, and so the cloud spending, whereas also being less likely to fully utilize the flexibility that is one of the public cloud’s key features.

Why Should One Use Private Clouds?
The following are the key reasons why businesses should adopt a private cloud server environment:
- SECURITY
Traffic to a private cloud is often limited to the organization’s transactions, and security is maintained. On the other hand, public cloud providers have traffic from millions of users and transactions at the same time, there is a higher probability of fraudulent traffic.
- REDUCED COST:
This flexibility and higher resource usage can not only facilitate enterprises’ performance. But also help them save money by maximizing the use of their servers.
A private cloud environment not only saves money over an on-premise environment, but it may also be more cost-effective than a public cloud environment for a few enterprises.
- PERFORMANCE AND COMPLIANCE
Companies may also use private clouds to accommodate constraints and rules imposed by national governments and business organizations. Many governments demand that their residents’ data to behold on servers that are physically located within their boundaries.
However, when a company can show the physical location of its data, compliance becomes a lot easier. Private Clouds, like Public Clouds, are ascendible.
- RESOURCE UTILIZATION
Virtualization technology, which supports all sorts of cloud computing, provides several of the benefits of personal cloud computing. Most servers are underutilized, and virtualization improves resource utilization for private cloud users by permitting workloads to be moved to a distinct physical server once service demands change.
Conclusion
On the whole, larger businesses are more likely to have their own IT infrastructure on-site. The benefits of a Private Cloud are numerous and noticeable. If your company is of a specific size and you operate in a business field that requires you to keep your sensitive data as well as that of your customers/clients. The benefits Public Clouds provide startups and smaller businesses far outweigh any potential concerns.